Optoelectronics products have received good feedback from major customers in North America
Recently, Shanghai Cambridge Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Cambridge Technology" or the "Company") held investor relations activities for specific targets and received research from many institutions. Cambridge Technology has been rooted in the communication industry for many years, and its initial products were mainly optical access terminals. Before the IPO in 2017, the company's product line gradually expanded to wireless access terminals. In 2018 and 2019, the company entered the field of high-speed optical modules by acquiring some assets, business and personnel of MACOM's Japanese subsidiary and some assets, business and personnel of Oclaro's Japanese subsidiary. After the completion of the above-mentioned mergers and acquisitions, the company established the Optoelectronics Division, planned and integrated the acquired assets and businesses, streamlined the organization and personnel, redeployed the production layout, and focused on high-end 400G/800G products. At present, although the company's optoelectronics business has not yet achieved profitability, it has gradually been on the right track.
The following is a summary of the Q&A of this investor event:
Q: The company's acquisitions are all of the assets of leading companies in Japan. Would you like to know the company's plans in terms of integration, product development and customer development?
A: Customers are mainly distributed in China and North America. Including several mainstream communication equipment manufacturers and data center operators, as well as many Tier 2 data center and equipment manufacturers. Some customers have already started mass supply, and some customers are still shipping and testing small batches. At present, there is still a big gap between the overall shipment volume and sales scale compared with the leading manufacturers in the industry. The company hopes to make some breakthroughs in the competition of 400G/800G products in the future.
Q: The company has acquired optical module technology for long-distance transmission from two Japanese companies it acquired. At present, what are the technical strengths of MACOM and Oclaro's Japanese subsidiaries and the company's technical layout?
A: Before the company's merger, the products and technologies of these two companies were mainly concentrated in the telecommunications field, mainly in the research and development, production and sales of high-speed medium and long-distance single-mode optical devices and optical modules. The transmission distance is generally 2 kilometers, 10 kilometers, 40 kilometers or even 80 km. In the field of data communication, these product technologies are only suitable for interconnection and transmission between data centers, not for short-distance transmission within 2 kilometers within a data center. After the company's acquisition, it began to venture into short-haul products such as the 500-meter DR4 for internal use in data centers. After that, the product line of optical modules will be further extended to various optical modules used in data centers. At present, the company's technical layout has been upgraded from the original 100G-based to 400G-based, and 800G products are being developed at the same time.
Q: We have noticed that the company has a relatively advanced layout in 800G and silicon photonics. Can you share your judgment on the future technology path and the progress of the company's high-speed product application of silicon photonics solutions?
A: The company is currently working on three major directions: (1) 800G (or even higher), EML or silicon photonics; (2) optical modules based on silicon photonics technology, 400G/800G or higher; (3) Coherent coherent technology, 400G/800G or higher. The three directions actually support each other. The most significant advantages of the silicon photonics solution are high integration, stable and superior working performance, and it is conducive to mass production. However, there are still some technical difficulties, especially the power consumption performance still has some gaps with the traditional EML solution, and some customer needs have a certain tendency.
Q: Whether it is 200G, 400G or the future 800G, the current concentration of electronic chip suppliers for the overall solution is very high. In the past year, the production capacity of chips has been a big problem. Both MACOM and Oclaro have relatively mature supply chains before. Is there any additional help for the company? Does the company have a multi-supplier layout in the supply chain and solutions of electronic chips?
A: The PAM4 DSP chips used in 200G and 400G are indeed highly concentrated. There are currently two suppliers of mature DSP chips. Lumentum/Oclaro's lasers lead the industry. MACOM's optical drives and TIAs, as well as APDs, are industry leaders. The company has subsidiaries in Shanghai, Japan and Silicon Valley of the United States, with R&D personnel and procurement personnel, and maintains good technical interaction and business relations with global suppliers. The company's DSP chips, lasers, optical drives, TIAs, etc. do not have supply problems. On the contrary, some other relatively small electrical devices sometimes have some supply problems.
Q: From the perspective of speed and distance, what different suppliers and solutions will there be for electronic chips in the future?
A: The development direction of electronic chips is relatively clear. The current performance is acceptable. The main development direction in the future is to reduce power consumption and improve interoperability. In the long run, new suppliers are bound to enter the market.
Q: MACOM and Oclaro mainly focus on carrier-grade high-speed and long-distance single-mode products. What are the common points and synergies in the technical path of data communication transmission with shorter distance but larger consumption?
A: The company entered the data center field because the historical accumulation of related technologies has certain advantages. On the one hand, although most of the data-pass optical modules are short-distance and non-airtight, their optical path design is the same as that of telecom optical modules. The strengths of MACOM and Oclaro include optical path design, simulation and selection and design of related optical path components. Now even some custom optical devices in the data pass optical module are modified on the basis of the original design, there will be some special designs, and the degree of customization and integration is relatively high. On the other hand, long-term telecom optical modules attach great importance to reliability, and relevant experience is also of great help to the development of digital optical modules.
Although the application environment of the data pass optical module is relatively stable, some functions may be removed due to cost considerations, such as the temperature control function, but this reduces the performance characteristics of the product to a certain extent. The reliability of the product in this case requires Historically accumulated design experience and design capabilities, including how to verify these designs, previous experience and capabilities will be very helpful.
In addition to the optical module inside the data center, the data communication optical module also has an optical module used in the interconnection of the data center. In fact, it is not very different from the original telecom optical module. After a simple modification, the telecom optical module can be applied to this Some applications.
Q: Compared with the two leading companies in the same industry, the company's profitability and stability are quite different. How does the company view it?
A: Lumentum decided to sell its optical module business at the beginning of its acquisition of Oclaro, and only maintain the original products. It was not until after the company's acquisition that it formulated strategies and deployed the R&D and production of new products according to market conditions and customer needs. However, it takes a long time for optical modules from product project approval, R&D design, sample delivery and testing, customer certification to mass shipment, and the production of products before the merger relies on a Thai foundry, and the operating expenses of the two Japanese subsidiaries are relatively high. Therefore, the company decided to integrate the two Japanese subsidiaries and transfer all production capacity to the Shanghai factory. In the meantime, the overall progress was repeatedly affected by the repeated outbreaks at home and abroad. The company's optoelectronics business has yet to reach economies of scale and break-even, but the company remains confident and has recently tested relatively well with several major customers in North America.
Q: What are the differences or advantages of the company's products and customer positioning compared with its friends? Which products are the company's good at, or which areas will the company focus more on?
A: One difference is that friends entered the telecommunications field from the datacom field, while the company is just the opposite. The data communication field is characterized by large volume, which makes price competition more intense. In the telecommunications field, the volume is small, but the unit price is higher and the profit is relatively good. For the company, the team that is limited to the telecom field is not enough to afford the current scale, and must expand to the data communication field.
On the one hand, major customers do not easily replace technical routes and suppliers, and friends and businessmen have already preconceived and solid status in the industry; on the other hand, as a late entrant, the company needs to wait for a suitable time window or actively participate in the opportunity to cater for technological iterations. In addition, the company also seeks to cooperate with telecommunication equipment manufacturers to broaden the sales channels of its products.
On the other hand, the company's product layout starts from high-end, mainly above 100G, including 200G and 400G. However, low-speed 10G, 25G and 40G are still the most demanded in the domestic and foreign markets. The demand for 200G and 400G is mainly concentrated in North American data centers, and domestic data centers are still in the early stage of large-scale deployment. The company's products in this low-speed optical module field are relatively lacking. This will have a great impact on the amortization of high-end products with relatively few shipments, and is also not conducive to eliminating fluctuations and undersaturation in production capacity. The product layout of friends and merchants is more complete and relatively more advantageous.
Although from the market point of view, the overall layout of the company's optical module business lacks low-end products, but in terms of the profitability of high-end single products, the gross profit margin is comparable to that of friends, and even the profitability of some products is slightly better. The company believes that it has a certain market competitiveness, which is also our confidence in insisting on making optical modules.
Q: Each company will have some competitive product lines. Which product line does the company think is more advantageous, and what is the rhythm of this product line’s heavy volume?
A: From a market point of view, in the traditional transition stage from 100G to 200G and 400G, in terms of modulation mode, from NRZ modulation to PAM4 modulation to coherent modulation, we focus more on PAM4 and future metro coherence.
At present, the single-wave 100G in the market expects some new product changes, which the company pays more attention to and is competitive. Judging from the bidding situation in the North American and Chinese markets, the company's products have technical and price advantages, and are also our flagship products. I am more confident in this.
Other traditional products such as CFP series, many companies may not do, these products are not very large, but the profit is better. The single profit of digital communication products is low, and it depends on the volume to support. From a quantitative point of view, some friends and businessmen are located in the central and western regions, and the labor and production costs are more advantageous than those in the coastal areas. We do not think that the labor cost is the final development direction of optical modules in the future. We must make use of our strengths and avoid weaknesses. Therefore, we I am more optimistic about the technological advantages. The product solution is the core, which ultimately determines the price competition. Currently, 800G, which can subvert the traditional design solution, I think will be the core point of seizing the market in the future.
Q: The demand for some hardware equipment by domestic cloud manufacturers is changing, and the company also makes some wireless access equipment. May I ask about the dynamic changes in the demand of domestic or overseas end customers, especially cloud manufacturers?
A: The current wave is mainly affected by the shortage of power chips. There is no shortage of optical chips in the whole series. Small fluctuations in chips may have a magnifying effect on the back end of the product, causing panic in the entire industry. The backlog of chip sellers and agents has further changed. The client's demand has not declined significantly, and even increased steadily.
Q: This year, everyone is upgrading 200G, 400G, including 100G DR1. Can you tell us about the trend of price changes?
A: The price of short-distance products is affected by the volume, and the data center is also more sensitive to the price. Not only 100G, but also the short distance of 400G, the price is getting closer and closer to the cost. The price of DR is close to the target change of $1/G, and the price of 400G DR4 is below the price target of $1/G.
 Detailed explanation of the relationship between the working distance of the collimator and the waist spot
Detailed explanation of the relationship between the working distance of the collimator and the waist spot
 Infinera and NEC partner to modernize Neutral Networks' fiber optic network
Infinera and NEC partner to modernize Neutral Networks' fiber optic network
 Optical module introduction
Optical module introduction
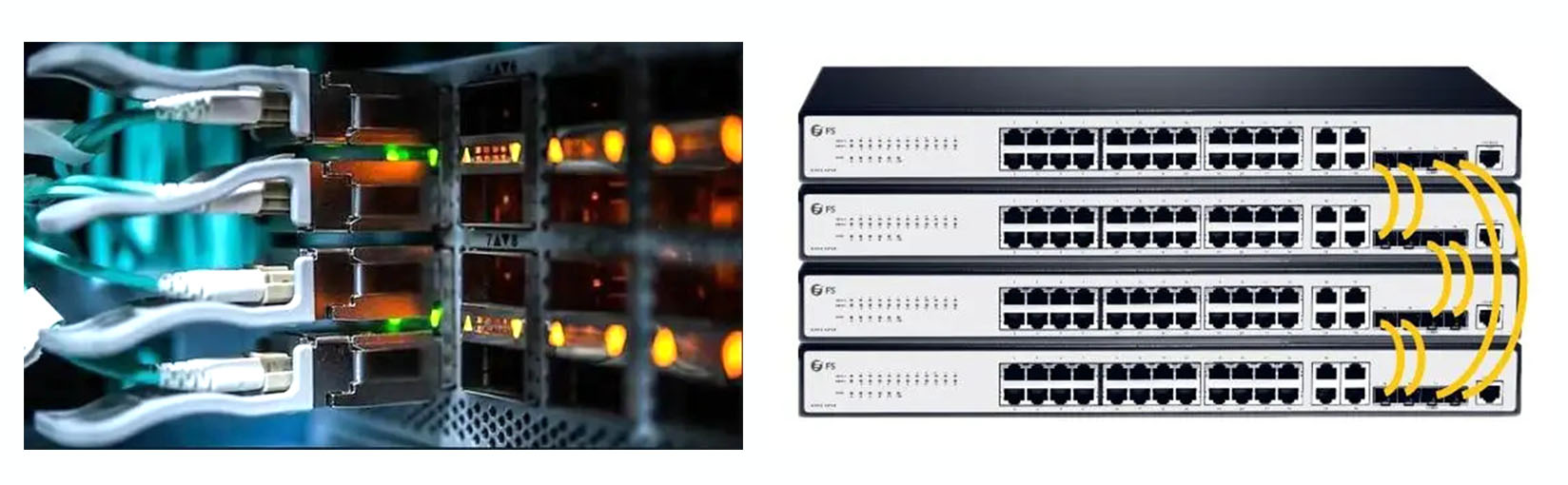 How to Select Optical Modules for Switch Stacking?
How to Select Optical Modules for Switch Stacking?








